The Aggregate Supply Curve Cannot Tell Us
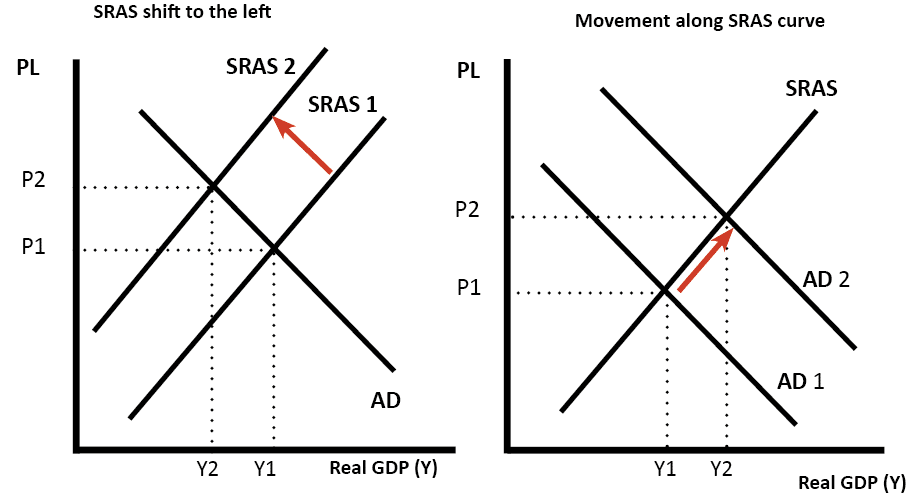
There are three ranges of the aggregate supply curve. When the AS curve shifts to the left then at every price level a lower quantity of real GDP is produced.
Aggregate Demand And Aggregate Supply Curves Article Khan Academy
REAL GDP SRAS SRAS SRAS PRICE LEVEL REAL GDP PRICE LEVEL REAL GDP PRICE LEVEL 5hat does it tell you about the relationship between the price level and real GDP if the SRAS is W.

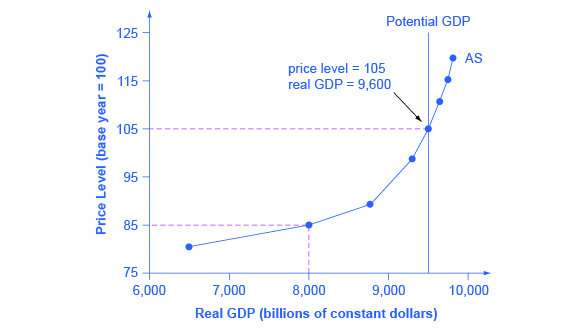
. The Three Ranges of the Aggregate Supply Curve on the ASAD graph. 36 The aggregate supply curve is obtained by. The phrase for some period of time alerts us to an important fact.
What causes the long run aggregate. The reasoning used to construct the aggregate supply curve differs from the reasoning used to construct the supply curves for individual goods and services. A Classical Range B Keynesian Range C Intermediate Range.
If there was an increase in investment or growth in the size of the labour force this would shift the LRAS curve to the right. We extract aggregate demand and supply shocks for the US economy from real-time survey data on inflation and real GDP growth using a novel identification scheme. The aggregate supply curve shows the various quantities of national output GNP produced or income GNI generated at different price levels.
Tells us what portion of consumption goods are imported. At this point you know both of the axis for the ASAD graph aggregate supply and demand graph. The Y axis is labeled PL and the X axis is labeled RGDP.
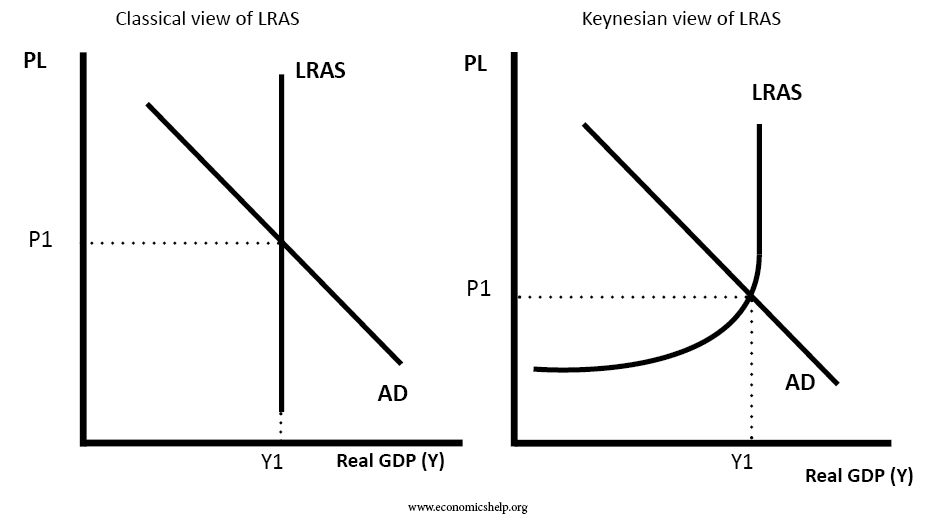
A shift in aggregate supply can be attributed to many variables including changes in the size and quality of labor technological innovations an increase in wages an increase in. C how the total dollar values of spending will ultimately be divided between output and prices. The aggregate supply curve cannot tell us how the total dollar values of spending will ultimately be divided between output and prices We draw the long-run aggregate supply curve as a vertical line to reflect the fact that.
When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level a greater quantity of real GDP is produced. What does this statement tell us about the shape of the long-run aggregate supply curve. A adding vertically the supply curves of all firms B adding horizontally the supply curves of all firms C adding the market supply curves of all goods and services D none of the above 37 The short-run aggregate supply curve is.
The Aggregate Demand Curve. Well talk about that more in other articles but for now just think of aggregate demand as total spending. The aggregate supply curve may not stand still for long.
The aggregate supply curve shows how much output is supplied by firms at different price levels. A curve that shows the relationship in. MGT 230 - If economic policy makers can keep the economy.
For this we need asked Apr 25 2020 in Economics by DangerousDana A. Cannot tell us how the total dollar values of spending will ultimately be divided between output and prices. C what the effect of changes in interest rates will be on real GDP.
Free markets allocate the supply of goods to the buyers who value them most highly a measured by their willingness to pay. The aggregate supply curve cannot tell us. The shape of the aggregate demand curve does NOT tell us anything about how the total dollar value of spending will ultimately be divided between output and prices.
Aggregate demand or AD refers to the amount of total spending on domestic goods and services in an economy. If wages or prices of other inputs change as they surely will during inflationary times then the aggregate supply curve will shift. However in special situations the SRAS may be very flat or very steep as shown below.
Thus given the quantity produced and sold in a. B how changes in the price level affect quantity demanded of all commodities. The aggregate supply curve depicts the quantity of real GDP that is supplied by the economy at different price levels.
The Long-run aggregate supply is vertical as it denotes that there is no relationship between the price level and potential GDP in the long run. These observations lead to two insights about market outcomes. Like the ordinary supply curve for an individual commodity the aggregate supply curve also slopes upward from left to right.
The supply curve for an individual good is drawn under the assumption that input prices remain constant. Tells us what portion of output is exported. Different factors explain the upward slope of the AS curve.
In this equation Y is output Ynatural is the natural rate of output that exists when all productive factors are used at their normal rates a is a constant greater than zero P is the price level and Pexpected is the expected price level. Strictly speaking AD is what economists call total planned expenditure. A the total of all planned production for an economy.
The short-run aggregate supply curve is affected by production costs including taxes subsides price of labor wages and the price of raw materials. This is a negative supply shock. Tells us what the employment level will be for any given level of output.
Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply. SHIFTS OF THE AGGREGATE SUPPLY CURVE. A downward sloping B always vertical C always horizontal.
The aggregate demand curve a. 92 4274 ratings Feedback Score View Profile. The equation for the short run aggregate supply curve is Y Ynatural a P - Pexpected.
Possible Shapes of Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve In general the SRAS has a positive slope. D anything about the quantity demanded of all commodities. Free markets allocate the demand for goods to the sellers who can produce them at the least cost.
The long run aggregate supply curve LRAS is determined by all factors of production size of the workforce size of capital stock levels of education and labour productivity. The aggregate supply curve cannot tell us. The LRAS is a vertical line when aggregate output is plotted against the price level.
This is called a positive supply shock. A how the total dollar values of spending will ultimately be divided between output and prices. Our approach exploits non-Gaussian features of macroeconomic forecast revisions and imposes minimal theoretical assumptions.
D is the total of all planned production in an economy. The aggregate supply curve shows. The relationship between this quantity and the price level is different in the long and short run.
So we will develop both a short-run and long-run aggregate supply curve. Which is more expensive concrete or asphalt per yard. Long-run aggregate supply curve.
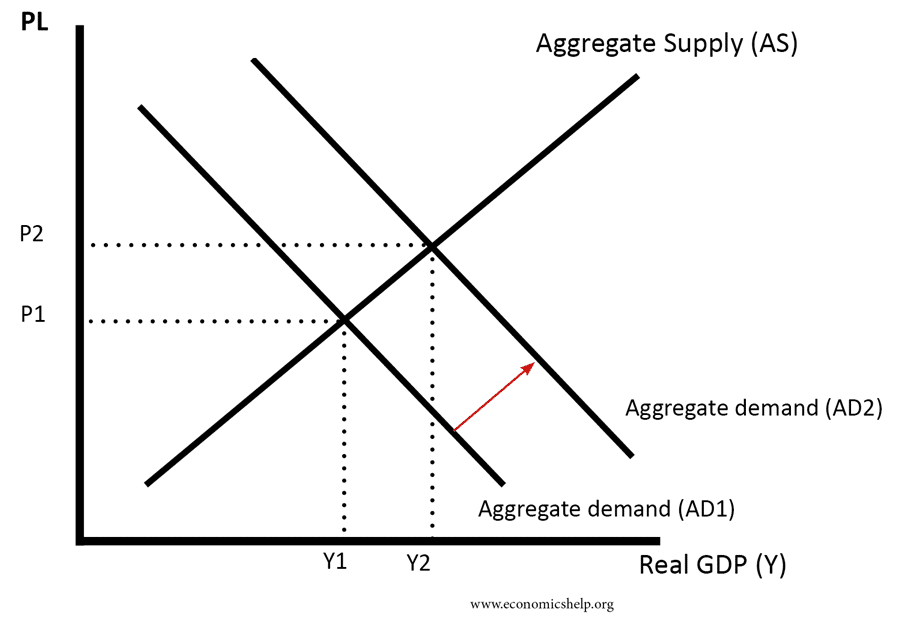
Shape Of Aggregate Supply Curves As Economics Help

Comments
Post a Comment